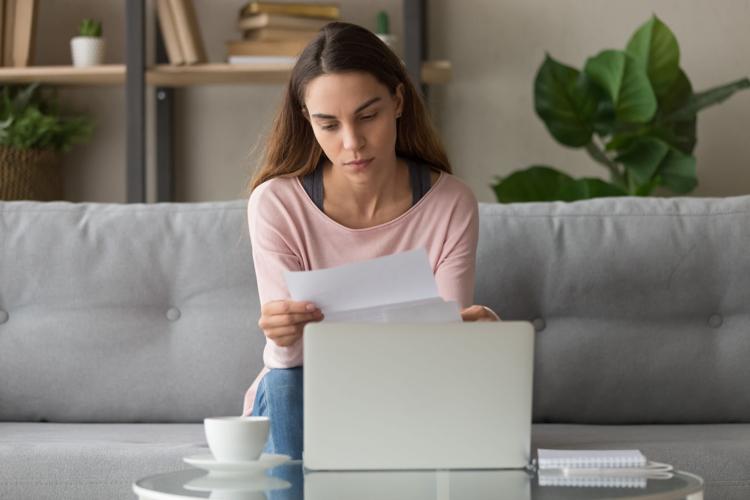
You’ve made it past the early action deadlines of Nov. 1 and Dec. 1. Yes, there are still the regular college application deadlines of Jan. 1 and Jan. 15, but the pressure is off. Now is a great time to get serious about scholarship opportunities. Let’s take a look at a financial aid glossary. Here is a vocabulary primer from to get you thinking about paying for college:
Academic year
One complete school year at the same school, or two complete half years at different schools. For schools that have a year-round program of instruction, nine months is considered an academic year.
Aid for military family service
Both the federal government and nonprofit organizations offer money for college to veterans, future military personnel, active duty personnel, or those related to veterans or active duty personnel
Annual taxable income
The amount of income used to determine how much tax you owe in a given year. This can include wages, salaries, bonuses, tips, investment income and unearned income.
Base year
When quantifying your income, the FAFSA uses information in your tax return from two years prior. This year is often referred to as the “base year” or the “prior-prior year.” For example, the 2021-2022 FAFSA will use income information in your 2019 tax return, so 2019 would be the base year or prior-prior year.
Credit
The amount of money you borrow and your ability to borrow to purchase goods and services. Credit is extended to you from a credit grantor with which you make an agreement to pay back the amount spent, plus applicable interest and fees, within an agreed-upon time.
Debt collection
The course of pursuing payments of loan debts due by borrowers.
Debt consolidation
A method of debt refinancing that involves taking out one loan to pay off others.
Default
Failure to repay a loan outlined in the agreed promissory note. Most federal student loan default occurs when a payment isn’t made in more than 270 days. It can result in legal consequences and a loss of eligibility for additional federal student aid.
Deferment
A temporary postponement of payment on a loan that is allowed under certain conditions and during which interest generally doesn’t accrue on certain types of subsidized loans.
Direct consolidation loan
This combines federal education loans into one loan for free via completion of the Federal Direct Consolidation Loan Application and Promissory Note. You will have a single monthly payment on the new Direct Consolidation Loan.
Direct PLUS loans
Federal loans that graduate or professional students and parents of dependent undergraduate students use to help pay for education expenses.
Direct subsidized loan
A federal student loan for which a borrower isn’t generally responsible for paying the interest while in an in-school, grace or deferment period.
Discretionary income
Used in determining a borrower’s eligibility for certain repayment plans and/or loan rehabilitation. It’s the difference between annual income and a percentage of the poverty guideline for the borrower’s family size and state of residence.
Early action
A college admission policy that allows applicants to apply and receive notice of their admission early. Applicants accepted under early action are not under a binding agreement to attend that school and may submit applications to other schools.
Early decision
A college admission policy that allows applicants who commit to attend a school to apply and receive notice of their admission early. If an applicant is accepted, he or she agrees to attend that school and must withdraw all other applications.
Emancipated minor
Someone who has been legally deemed an adult by a court in his or her state of residence. If you are an emancipated minor, you are considered an independent student and will not provide information about your parents on the FAFSA form.
Endorser
Someone who agrees to repay the Direct PLUS Loan if the borrower becomes delinquent in making payments or defaults on the loan. The endorser may not be the student on whose behalf a parent obtains a Direct PLUS Loan.
Enrollment status
This is reported by the school you attended and indicates whether you are, or were, full-time, three-quarter time, half-time, less than half-time, withdrawn, graduated, etc.
Extended repayment plan
This allows you to repay your loans over an extended period. Payments are made for up to 25 years. There are specific eligibility requirements to qualify for this plan.
Family size
This doesn’t mean people who physically live with you. It’s about who you support financially. If you do not financially support anyone, you will just put 1 for yourself.
Federal Pell grant program
The Pell Grant is the largest federal grant program offered to undergraduates. It is designed to assist students from low-income households. To qualify for a Pell Grant, a student must demonstrate financial need by completing and submitting the FAFSA form.
Federal student aid
Aid from the government in the form of grants, loans and/or work-study to assist students with college or career school. Students have to complete the FAFSA form to apply for this aid.
Federal supplemental educational opportunity grant
A grant awarded to an undergraduate student who demonstrates exceptional financial need to help pay for their education. Awards can range from $100 to $4,000 and do not need to be repaid.
Federal work study
A program that provides part-time jobs for students with financial need. The program encourages community service work and work related to your field of study. To receive funds, you will need to be awarded work study and secure a job.
Forbearance
A period of time when your monthly loan payments are temporarily stopped or reduced. Interest will continue to be charged on your loans. Be aware that unpaid interest may be capitalized (added to your loan principal balance) at the end of your forbearance period.
FSA ID
This consists of a username and password that give you access to the Department of Education’s online systems and can serve as your legal signature when completing electronic documents.
Head of household
For tax purposes, you might claim head of household if you are unmarried and responsible for more than half of the cost of keeping up your and your dependent’s home.
Income-based repayment plan
Eligible loans: Direct Loans and FFEL Program Loans other than those in default, PLUS Loans made to a parent borrower, or Consolidation Loans that repaid a Direct or Federal PLUS Loan made to a parent borrower. Consolidating a Federal Perkins Loan may make you eligible.
Income-contingent repayment plan
Eligible loans: Direct Loans other than those in default and Parent PLUS Loans. Consolidating a Federal Perkins Loan, FFEL Program Loan or Direct PLUS Loan made to a parent may make you eligible.
Independent student
A student who is at least 24 years old, married, a graduate/professional student, a veteran, a member of the armed forces, an orphan, a ward of the court, someone with legal dependents (not a spouse), an emancipated minor, or someone who is or at risk of being homeless.
Iraq and Afghanistan service grant
You may be eligible for the IASG if your parent or guardian died as a result of military service performed in Iraq or Afghanistan after the events of 9/11, and you are not eligible for a Federal Pell Grant.
Judgment lien
This gives a creditor the legal right to keep property when the owner fails to pay a debt. It can only be granted by a court. A student (or parent in the case of a parent borrower) with a judgment lien will not qualify for federal student aid.
Legal guardianship
A designation by a court that authorizes someone to care for an individual in place or absence of parents. Having a legal guardian qualifies you as an independent student, such that you do not have to report your parents’ income on the FAFSA form.
Loan discharge
The removal of a borrower’s obligation to repay a loan under certain circumstances including but not limited to death, disability, bankruptcy, fraud and identity theft.
Loan forgiveness
Student loan forgiveness is offered to encourage certain types of employment. A loan may be fully or partially forgiven after a certain number of years of qualifying employment.
Master promissory note
An MPN is a legal document that contains the borrower’s rights and responsibilities and terms and conditions for repayment. Direct PLUS and Direct Subsidized/ Unsubsidized Loans have different MPNs.
Merit-based
Merit-based means something is based on a student’s ability. For example, a merit-based scholarship might be awarded based on a student’s high grades.
Offset
When a payment from the Department of Treasury (such as an income tax refund) is reduced or stopped to pay off a delinquent debt. The remainder of a refund will be processed; an offset shouldn’t delay it unless the entire refund is applied to the debt.
Ombudsman group
A group dedicated to helping resolve disputes related to the federal student aid programs.
Partial financial hardship
An eligibility requirement under the Income-Based Repayment and Pay As You Earn repayment plans.
Pay as you earn plan
A repayment plan with monthly payments that are generally equal to 10 percent of your discretionary income, but never more than the 10-year standard repayment amount.
PLUS credit counseling
This helps graduate/professional students and parents of eligible dependent undergraduate students understand the obligations associated with borrowing a PLUS Loan and assists them in making careful decisions about taking on student loan debt.
Prepaid tuition plan
Also known as a section 529 plan, this lets you lock in future tuition rates at in-state public colleges at current prices and is usually guaranteed by the state in which the plan was established.
Proprietary school
A private, for-profit school that provides education and training.
Public service loan forgiveness help tool
This tool will help you understand the following about the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program: what is required to participate, if an employer qualifies, which loans qualify, and other actions to take to receive PSLF.

Public service loan forgiveness program
This program forgives the remaining balance on your direct loans after you have made 120 (10 years) qualifying monthly payments under a qualifying repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Regular student
A student who is enrolled or accepted for enrollment at an institution for the purpose of obtaining a degree, certificate or other recognized education credential. To be eligible for federal student aid, you must generally be a regular student.
Rehabilitated loan
Loan rehabilitation is one method of getting your student loan out of default. To begin the rehabilitation process, you must contact your loan holder. If you’re not sure who your loan holder is, log in to your account to get your loan holder’s contact information.
Revised pay as you earn plan
A repayment plan with monthly payments that are generally equal to 10 percent of your discretionary income.
Room and board
The cost of housing and food while attending college or career school.
Satisfactory academic progress
The process a school uses to determine if a student is meeting all of his or her educational requirements and is on target to graduate on time with a degree or certificate. This process may vary across schools.
Scholarships
Gifts that don’t have to be repaid and are designed to help students pay for an undergraduate degree. They can be a one-time gift or renewable, depending on the scholarship.
Service obligation
A Service Obligation signing is an agreement to teach full-time, in a high-need field, at an elementary/secondary school/educational service agency for low-income students, and for at min 4/8 academic years following their ending of the grant-assisted study.
Standard repayment plan
The basic repayment plan for the William D. Ford Federal Direct Loan (Direct Loan) and Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) programs. Payments are fixed and made for up to 10 years (10 to 30 years for consolidation loans).
State aid
States offer financial assistance to eligible residents to help reduce educational costs. Some state aid is first come, first served, so complete your FAFSA form early. Contact your state grant agency for more information.
Student fraud
Any situation where an individual falsifies information in order to qualify for student aid. Examples of student fraud include using false information on the FAFSA, such as income or marital status, or reporting an invalid high school diploma.
Student loan debt burden
The percentage of a borrower’s monthly income that is dedicated to his or her student loan payments. The smaller this percentage, the lower the debt burden.
TEACH grant
This grant funds students who are completing or plan to complete coursework that is required to be a teacher, and who agree to teach full-time in a high-need field at an educational service agency or school for low-income students for at least four years.
TEACH grant initial and subsequent counseling
This process acquaints the student to the TEACH Grant program and the TEACH Grant service obligation.
Teach-out plan
A written agreement among schools that provides for the equitable treatment of students and a reasonable opportunity for students to complete their program of study if a school ceases to operate before they have completed their program of study.
Total and permanent disability discharge
This relieves you from having to repay your federal student loan(s) and/or complete your Teacher Education Assistance for College and Higher Education (TEACH) Grant service obligation.
Tuition
The amount of money you owe for receiving instruction, materials, and/or supplies, or for the rental or purchase of equipment, for a course of study at your institution.
Unsubsidized loan
An unsubsidized loan borrowed through the Direct Loan Program offers students a low, fixed interest rate and flexible repayment terms. It is not based on financial need. The borrower is responsible for paying all the accumulated interest, until the loan balance is paid off.
Untaxed income
Income you don’t pay taxes on, such as Supplemental Security Income, child support, or federal or public assistance.
William B. Ford direct loan program
The program under which eligible students and parents borrow directly from the Department of Education at participating schools. Loans include Direct Subsidized, Direct Unsubsidized, Direct PLUS, and Direct Consolidation Loans.